“Suppose,” the American author and humorist Mark Twain once said, “you were an idiot. And suppose you were a member of Congress. But I repeat myself.” The United States House of Representatives, which can’t agree on gun control legislation or pretty much anything, makes it a priority in the doldrums of a Washington summer to weigh in on issues sparked by allegations of doping in international sport?
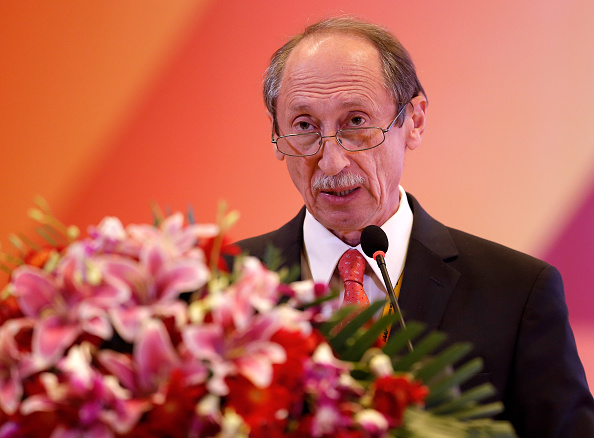
The House Committee on Energy and Commerce sends a letter to the International Olympic Committee president, Thomas Bach, just days before a World Anti-Doping Agency-commissioned report into allegations of state-sanctioned doping in Russia? For what purpose?
Here is the answer: once again, to highlight the ridiculous inconsistencies and political posturing all around, and in particular from the committee, chaired by Representative Fred Upton, a Republican from Michigan.
Mr. Upton represents Michigan’s 6th District, in the southwestern corner of the state. His district includes Berrien County. At that county courthouse on Monday, according to authorities, an inmate grabbed a deputy’s gun and shot four people, two — both retired police officers — fatally.
On Tuesday, Mr. Upton sends out a letter to the IOC president?
From the letter: “Athletes worldwide, including those that will participate in the upcoming Rio Olympic Games, must have confidence that their sports are completely free of doping and that all governing bodies in international sport are doing everything possible to ensure that result.”
This is wishful thinking. Completely free of doping is never going to happen. Repeat, never. “Zero tolerance,” like Nancy Reagan’s “just say no,” is empty rhetoric, for two reasons: one, doping works and, two, elite athletes want to win. Including Americans. See, for instance, Marion Jones and Lance Armstrong, among many others.
At any rate, who appointed the U.S. House the moral, legal and ethical guardian of “athletes worldwide”?
Next sentence: “To ensure the integrity of the Olympic Games, we need assurances from sports’ international governing bodies in the form of decisive actions, not just words. The failure to do so is simply irresponsible and we will not remain silent.”
For sure, when it comes to being irresponsible, sanctimonious and hypocritical, Congress has that down. An awful shooting on Monday. The “decisive action” of a letter to the IOC president on Tuesday.
Beyond which, and again — it is not, repeat not, the mandate of the United States Congress to “ensure the integrity of the Olympic Games.” Anymore than it is the province of the Japanese Diet, Russian Duma or Israeli Knesset.
If Mr. Upton or his committee might ever seriously be inclined to take “decisive action,” here’s a concrete suggestion:
Stop talking the talk and start walking the walk: find some real money to advance the anti-doping campaign, either within the United States or, on the spurious grounds that this particular House committee has any extra-territorial reach, with its friends (or not) in other governments.
WADA’s 2016 budget is $26.3 million. The United States government contributed $2.05 million. That’s not even 10 percent. Yet Congress wants to play big dog? Absurd.
For 2016, the U.S. federal government expects to take in $2.99 trillion and spend $3.54 trillion. Whichever number you want to use as the denominator — $2 million is an almost infinitesimal fraction.
Here are some other numbers:
Major U.S. college athletic departments run with revenues way, way, way bigger than WADA. Texas A&M, for instance, took in $192 million in operating revenue during its 2014-15 fiscal year. Oregon reported $196 million in 2013-14.
A real difference-maker would be to get that kind of money for the anti-doping effort.
China gave all of $286,365 toward WADA’s 2016 revenues. The United States led the London 2012 medal count. Second? China. The Chinese can’t give more than $286,365?
Kenya, the powerhouse of distance running, also now under keen suspicion for doping issues? The Kenyan government gave WADA a grand total of $3,085. That’s three-thousand-eighy-five. Not $3.085 something. Exactly $3,085.
That Usain Bolt guy? Jamaica contributed precisely $4,638.
Peru? Where, in Lima, the IOC is due to hold its general assembly next year? WADA has invoiced the government of Peru $20,853 for 2016. Total received, as of July 8: zero.
Qatar? Where the 2022 soccer World Cup is going to be staged? Where natural gas made Qatari citizens the world’s richest in a generation, and where a number of leading U.S. universities now have branch campuses? Qatar was invoiced $70,438. They have paid.
The Japanese government contributed $1.5 million, in the ballpark with the American contribution. Do you hear the Japanese — hosts of the 2020 Tokyo Games — writing a same or similar letter to the IOC? Curious.
The governments of Germany, France, the United Kingdom and, yes, Russia contributed the exact same amounts: $772,326 apiece.
The British, too, have a tendency to hold Parliamentary hearings on matters that do little but serve as kabuki theater — for instance, hauling Seb Coe, the president of track and field’s international governing body, the IAAF, into Westminster in a bid to score political points.
As for the French and Germans? Their legislative bodies have more important things to do. Like, maybe, in the wake of Brexit, keeping the European project together.
A letter like the one from Mr. Upton accomplishes precisely nothing.
At least nothing constructive.
To be brutally frank, it holds the risk for real damage in potentially undercutting the Los Angeles bid for 2024, the very thing that actually could effect real change if not bring a well-deserved spotlight throughout the United States, and beyond, to the many ways the Olympic movement — and the anti-doping campaign in particular — could be improved by reform.
To be clear: there has not been a Summer Games in the United States for 20 years now, since Atlanta in 1996. The last Winter Games? Salt Lake City, 2002.
If LA wins, it will be a generation since the Games came to the United States.
And yet Congress is playing busybody?
The only good news: there haven’t been demands for congressional hearings.
This is something of a change.
Because this, for those with a ready sense of history, and rest assured there are many members of the IOC with a keen sense of history indeed, is not Mr. Upton’s first go-around in seeking to leverage the Olympic movement for headlines and political attention-seeking.
He and Senator John McCain, the Republican from Arizona who for years has been the leading force on the Senate’s Commerce Committee — the two panels with oversight over the U.S. Olympic Committee — pop up with regularity, like whac-a-moles at the county fair, when it’s seemingly to their advantage to put the Olympic rings is in the spotlight.
A June 20 letter from that Senate committee to WADA president Craig Reedie went out from the current chairman, John Thune of South Dakota. But you have to be naive to the max to think that McCain wasn’t involved.
And why wouldn’t he be?
McCain is up for election in November. The Olympic movement makes for a convenient target.
Since McCain is himself an avowed student of history, you’d think maybe he would understand that all actions carry consequences.
Let’s dial the wayback machine to the late 1990s, and the scandal tied to Salt Lake’s winning 2002 bid.
According to published minutes from the IOC’s policy-making executive board, its members often expressed considerable friction when it came to Congress and, by extension, the USOC.
As well, and in the context of the current focus on Russia, it’s something of a case of pot, kettle, black or, if you prefer, glass houses — the minutes showing the United States being accused of being inconsistent in the fight against athletes’ use of illicit performance-enhancing substances.
A number of IOC members and staffers, to quote from the story that I wrote on this very issue for the Los Angeles Times in February 2002, said they believed U.S. officials had not been forthcoming in disclosing positive drug tests — in particular, the matter of a U.S. track star allowed to run at the 2000 Sydney Games despite a positive test for a banned steroid. It wasn’t until 2003 that the LA Times reported that athlete was the 400-meter standout Jerome Young.
Indeed, at the public IOC session immediately before the opening of the Salt Lake Games, here was the longtime Canadian IOC member Dick Pound calling on international track and field officials to expel USA Track & Field for refusing to disclose the names of athletes with positive tests. What do you know? U.S. officials consistently denied any wrongdoing.
In the 2016 context, it is well worth noting what Bach said Wednesday when asked about the Russians. He observed, “The right to individual justice applies to every athlete in the world.”
He also said, and if anyone in Congress would pay attention amid what increasingly seems like a rush to demonize everything Russian, Bach was essentially espousing one of the fundamental principles of American justice: “Everybody not implicated cannot be made responsible for the misbehavior of others.”
Pound, meanwhile, served as the first WADA president. Now there are cries that Reedie has a conflict of interest because, just like Pound, he is a senior IOC member and serving WADA as well? Where were those conflict cries when Pound was president?
The reason men like Reedie and Pound serve interlocking directorates within the Olympic sphere is simple: it takes years to understand the politics, finance, diplomacy and culture that attends international sport, in particular the Olympics. Evidence? The USOC hired an outsider, Stephanie Streeter, as CEO in 2009. She stayed for a year, forced out because she didn’t — couldn’t — understand.
When Pound a few months ago delivered the independent WADA-appointed commission report accusing the Russians of multiple wrongdoings, he was widely hailed as a hero. No thorough examinations of the potential for conflict because of his IOC and WADA ties? Curious.
Amid the Salt Lake scandal, both McCain and Upton formally demanded that then-IOC president Juan Antonio Samaranch testify before Congress.
An influential Belgian IOC member at the time, Prince Alexandre de Merode, for years a leader in the anti-doping effort, declared McCain’s letter “extremely arrogant,” saying, “The IOC did not have to justify itself to the United States.”
The then-senior Chinese IOC delegate He Zhenliang, according to those IOC minutes, said he did not wish to “comment on [Upton’s] knowledge about the contemporary world nor pass judgment on his IQ. But what [He] could not ccept was the manner in which [Congress] was treating the IOC, a supranational organization, namely as if they were servants in his house. Such arrogance was unacceptable.”
Jacques Rogge, also of Belgium, said Samaranch ought not testify voluntarily “under any circumstances.” He said, “Despite good preparation and support, this would be bad PR and would be an ambush by the USA.”
Samaranch did end up testifying, in December 1999. It proved not an ambush. He played wise international diplomat.
Rogge went on to become IOC president in 2001, serving until 2013. What happened to American interests in the Olympic movement during his 12 years? Politically, the U.S. was marginalized. Economically, a huge rift erupted over USOC shares of Olympic revenues. Baseball and softball? Axed from the Games. New York’s bid for the 2012 Games? Lost big, in 2005, to London. Chicago’s 2009 bid for 2016? Lost big, in 2009, to Rio.
Bach has been president now for nearly three years. He learned a great deal about how the IOC works from observing, and working closely with, none other than Samaranch.
“We look forward,” Upton’s letter concluded, “to working closely with IOC, WADA and others toward this end,” a reference to the call for “assurances” regarding Olympic integrity.
Good luck with that, congressman. Olympic integrity is assuredly a good thing. But why would the IOC want to work with you? Better you should brush up on your reading before you prove the master right again, for Twain also observed, “All congresses and parliaments have a kindly feeling for idiots, and a compassion for them, on account of personal experience and heredity.”